Hexamer calculation.
Mutations in proteins from the Canser Genome Atlas, their effect on the stability of the hexameric complex
Familiarize yourself with the main list of calculations.
Step-by-step approaches in checking the correctness of building X-ray structures (PDB files)
Biomarker development concept

Affinity-targeting schemes for protein biomarkers
The discovery of cancer at an early stage improves treatment outcomes, yet cancer detection thresholds based on measuring the abundance of biomarkers produced by small tumors are biologically limited. Here we develop a mathematical framework to explore the use of activity-based biomarkers for early cancer detection.
The expression of a transcription factor of interest, like all other cellular proteins, is itself transcriptionally controlled by transcription activators or repressors (other transcription factors or itself in a positive or negative retro-control) and by epigenetic DNA or histone writers/readers/erasers.
number condition
5.46825768554032
5.46825768554032
max eigenvalue
4.484534e-19
4.484534e-19
min eigenvalue
1.52566e-24
1.52566e-24
error computational SVD
1.8869270e-31
1.8869270e-31
'7eg8_6_taf4.pdb','7eg8_6_taf5.pdb','7eg8_6_taf8.pdb','7eg8_6_taf9.pdb','7eg8_6_taf10.pdb','7eg8_6_taf12.pdb','80'

Checking the correctness of the PDB file.
PDB file's names

Determination of the computational error of the SVD

Comparison of calculated data for two identical PDB structures obtained in different laboratories.


Iter.
0
1
2
3
4
0
1
2
3
4
F-count
1
29
31
43
45
1
29
31
43
45
f(x)
1.740260e-19
1.156085e-08
1.985202e-08
1.755506e-08
1.709531e-08
1.740260e-19
1.156085e-08
1.985202e-08
1.755506e-08
1.709531e-08
Feasibility
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
0.000e+00
First-order optimality
1.104e-06
3.528e-01
4.174e-01
3.740e-01
3.925e-01
1.104e-06
3.528e-01
4.174e-01
3.740e-01
3.925e-01
Norm of step
1.731e-07
1.089e-07
7.008e-09
7.276e-10
1.731e-07
1.089e-07
7.008e-09
7.276e-10
A
max RMSD __________________Optimal value of the function____________First-Order Optimality Measure
6.318e-13_______________________________1.7095305e-08_____________________________________3.925035e-01
6.318e-13_______________________________1.7095305e-08_____________________________________3.925035e-01
TFIID SUB-COMPLEXES. Arrows indicate transcription start site. (A) A TAF1/TAF2 complex contacts Initiator at a TATA-less promoter. (B) TAF1 contacts a downstream promoter element (DPE) at a TATA-less promoter. TAF4 is also important for this interaction. (C) TAF4B substitutes for TAF4 in a TFIID complex bound at a TATA-box by TBP.
[Targeting TBP-associated factors in ovarian cancer]
[Targeting TBP-associated factors in ovarian cancer]

The realization that TFIID subunits regulate cellular processes in tissue-specific manners prompted research into TAF involvement in modulating tumor characteristics, including proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, metastasis, and hormone response. The considerable variability seen in these reports, which are summarized in Table 1, further supports the notion that the plasticity of the TFIID complex allows for variation in transcriptional control depending on cellular context. However, perhaps due to this plasticity, our understanding of the contribution of the TFIID complex to tumorigenesis and cancer progression remains limited.

Symbol:TAF12
Name: TAF12 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 20kDa
Synonyms:TAF2J
_______________TAFII20
Name: TAF12 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 20kDa
Synonyms:TAF2J
_______________TAFII20
The structure of the geksamer indicating the substitutions of amino acid residues in proteins
Symbol:TAF4
Name: TAF4 RNA polymerase II,
TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 135kDa
Synonyms:TAF2C
________________TAF2C1
________________TAF4A
________________TAFII130
________________TAFII135
Name: TAF4 RNA polymerase II,
TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 135kDa
Synonyms:TAF2C
________________TAF2C1
________________TAF4A
________________TAFII130
________________TAFII135

TAF12
TAF4
TAF9
TAF5
TAF10



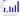
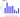

Symbol:__TAF8
Name:____TAF8 RNA polymerase II,
______________TATA box binding protein (TBP)-______________associated factor, 43kDa
Synonyms:FLJ32821
________________TAF(II)43
________________TBN
NCBI Gene:129685
UniProtKB:_Q7Z7C8
Name:____TAF8 RNA polymerase II,
______________TATA box binding protein (TBP)-______________associated factor, 43kDa
Synonyms:FLJ32821
________________TAF(II)43
________________TBN
NCBI Gene:129685
UniProtKB:_Q7Z7C8












B
Upregulated in colon cancer cell lines with RAS mutations or overexpression of mutant RAS; knockdown destabilizes TFIID; and enhances E-cadherin levels, thereby reducing migration/adhesion of RAS transformed cells with EMT





Symbol:TAF5
Name:TAF5 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 100kDa
Synonyms:TAF2D
_______________TAFII100
Name:TAF5 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor, 100kDa
Synonyms:TAF2D
_______________TAFII100
The structure of the geksamer indicating the substitutions of amino acid residues in proteins
AA change: S492L
¹ of Case:1dead
Desease type:
ductal and lobular
neoplasm
¹ of Case:1dead
Desease type:
ductal and lobular
neoplasm
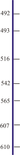
AA change: T493A
¹ of Case:1/alive
Desease type:Transitional
cell papillomas and
carcinomas
¹ of Case:1/alive
Desease type:Transitional
cell papillomas and
carcinomas
AA change: I516T
№ of Case:1/ 0
Desease type: cystic,
mucinous and
serous neoplasm
№ of Case:1/ 0
Desease type: cystic,
mucinous and
serous neoplasm
AA change: H542Y
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas
AA change: G565E
№ of Case:1/0
Desease type: plasma
cell tumors
№ of Case:1/0
Desease type: plasma
cell tumors
AA change: R607Q
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas
AA change: R610Q
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas
№ of Case:1/ Alive
Desease type:
adenomas and
adenocarcinomas

The structure of the geksamer indicating the substitutions of amino acid residues in proteins

TAF12
TAF4
TAF9
TAF5
TAF10


C

TBP-ASSOCIATED FACTOR ALTERATIONS IN HIGH-GRADE SEROUS OVARIAN CANCER (HGSC). (A) Cross-cancer summary of copy number alterations and mutations in TAFs for all cancer sets in the cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics . (B) Amplifications, copy number gains, and mRNA upregulation of TAF2, TAF4, and TAF4B, and deletions and mRNA downregulation of TAF9, in the cBioPortal HGSC set (TCGA, provisional, complete tumors). These “oncoprints” are partial views of alterations in 158 complete tumors. Alterations are present in 158 complete tumors in the percentages noted on the left.[Targeting TBP-associated factors in ovarian cancer]
General graph representing a summary graph of substitutions in proteins forming a hexamer

Symbol: TAF10
Name: TATA-box binding protein associated factor 10
Synonyms: TAF2A
__________________TAF2H
__________________TAFII30
NCBI Gene 6881
UniProtKB Swiss-Prot Q12962
Name: TATA-box binding protein associated factor 10
Synonyms: TAF2A
__________________TAF2H
__________________TAFII30
NCBI Gene 6881
UniProtKB Swiss-Prot Q12962
T127M
Cases:0/1
Squamous cell neoplasms
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
Cases:0/1
Squamous cell neoplasms
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
F144V
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
D148Y
Cases:1
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
R150H
Cases:1/1
Squamous cell neoplasms
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/1
Squamous cell neoplasms
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
R153Q
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Q160H
Cases:1/0
Squamous cell neoplasms
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
Cases:1/0
Squamous cell neoplasms
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
K161T
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
N168D
Cases:1
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
Cases:1
cystic, mucinous and serous neoplasms
L171I
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
C174W
Cases:1
Ductal and lobular neoplasms
Cases:1
Ductal and lobular neoplasms
G208V
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
Cases:1/0
Adenomas and Adenomacarcinomas
P214L
Cases:1
Ductal and lobular neoplasms
Cases:1
Ductal and lobular neoplasms


See figure below
D

