Tubulin Inhibitors: Decades of controversy
The interaction of Rigosertib (ON-01910) with Tubulin has been studied since the early 2010s, with some initial reports around 2012-2014 suggesting that rigosertib may function as a microtubule destabilizer.
In the last decade, conflicting data on the effectiveness of Rigosertib have accumulated. The effectiveness of Rigosertib in vitro was achieved (or not achieved) only at elevated concentrations 10 mkM -50 mkM of the inhibitor compared to the effectiveness (nM)
in vivo experimental cell lines.
Also, special attention was paid to the purity of the obtained preparations, which contain a small amount of chemically active substances ON01500. A typical batch of clinical material is 99.9% pure and could include 0.1% of these impurities. Several storage conditions, including higher temperature, acidic pH and exposure to intense light can lead to the degradation of rigosertib into ON01500. Rigosertib purchased from Selleckchem contained approximately 5% of ON01500 as well as a few additional contaminants, while clinical grade Rigosertib obtained from Onconova Therapeutics had undetectable amounts of these contaminants.

[A Contaminant Impurity, Not Rigosertib, Is a Tubulin Binding Agent]
Determination the tubulin efficiency inhibitors by calculation methods.
However, debates about its actual mechanism of action persisted. There is some controversy surrounding the effect of rigosertib on microtubule assembly, as the concentration of rigosertib required for in vitro experiments is much higher to destabilize microtubules, compared to in vivo experiments, where a much lower concentration is required to destabilize microtubules.Some of the researchers claim that It is also important to note that many microtubuledestabilizing agents require substantially higher concentrations in vitro for robust microtubuledestabilizing activity as compared to cell culture.
Below is a summary table highlighting key studies, their methodologies, rigosertib concentrations used, and the corresponding findings:


Part 1.2. How to put an end to the effectiveness of tubulin inhibitors?
The topic of the second video: Determining the efficiency of tubulin inhibitors using computational methods.Tubulins form various molecular formations in solution as they reach thermodynamic equilibrium. The study of the thermodynamic equilibrium of molecular formations in solution is the objective of our research. The results of the computational studies presented in this video were performed using the open AI platform on the Binomlabs website, the link is in the description under the video.
[Mechanism of action of rigosertib does not involve tubulin binding]
Stacey J. Baker, Stephen C. Cosenza, Saikrishna Athuluri-Divakar, M.V. Ramana Reddy, Rodrigo Vasquez-Del Carpio, Rinku Jain, Aneel K Aggarwal, E. Premkumar Reddy
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.12.874719
Wild-type and TUBBL240F-expressing cells failed to proliferate in the presence of clinical grade rigosertib at concentrations that are lethal to wild-type cells
Purified preparation of Rigosertib obtained from Onconova (O-RGS) shows little or no tubulin depolymerizing activity at doses up to 50µM.
Rigosertib purchased from Selleckchem (S-RGS), on the other hand, exhibits depolymerizing activity when used at concentrations above 25µM, reaching complete depolymerization at a concentration of 100µM (Fig. 1D), suggestive of the effect of the impurity.
Expression of the L240F beta-Tubulin mutant provides resistance to Rigosertib, suggesting that tubulin binding is critical to its cytotoxic activity. For these experiments, Jost et al. (2017) prepared lentiviral constructs that encoded empty vector or wildtype (wt) TUBB or TUBB L240F, which were individually transduced into wt K562, HeLa, or H358 cells.
[Mechanism of action of rigosertib does not involve tubulin binding]
[Mechanism of action of rigosertib does not involve tubulin binding]
С другой стороны, ригосертиб, приобретенный у Selleckchem (S-RGS), проявляет деполимеризующую активность при использовании в концентрациях выше 25 мкМ, достигая полной деполимеризации при концентрации 100 мкМ (рис. 1D), что свидетельствует о влиянии примеси.
M. Jost, Y. Chen, L.A. Gilbert, M.A. Horlbeck, L. Krenning, G. Menchon, A. Rai, M.Y. Cho, J.J. Stern, A.E. Prota, et al.
[Combined CRISPRi/a-Based Chemical Genetic Screens Reveal that Rigosertib Is a Microtubule-Destabilizing Agent]
Mol. Cell, 68 (2017), pp. 210-223
O-RGS using this technique, we were unable to detect binding even at a concentration of 50µM
[A Contaminant Impurity, Not Rigosertib, Is a Tubulin Binding Agent]

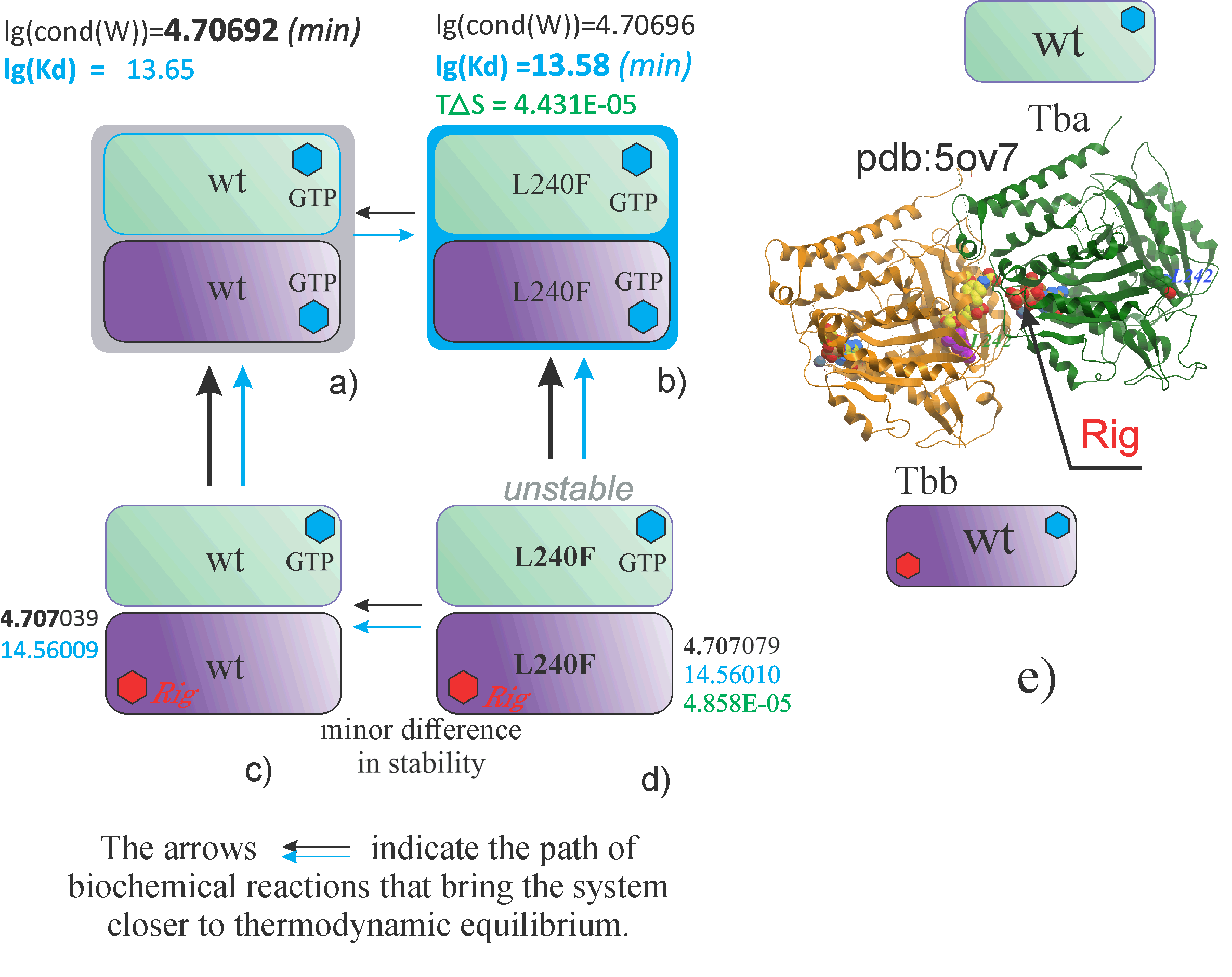
The complexity of the analysis of the effect of mutation on tubulin binding to rigosertib is that wild-type tubulins are slow to attach a rigosertib molecule, and mutant forms are even less susceptible to rigosertib.
Figure A shows a dimer of the wild-type tubulins alpha and beta, containing two small molecules of guanosine triphosphate.
Above the dimer, two calculated values are given - the stability parameter lg(cond(W)) and the dissociation constant lg[Kd].
The first parameter lg(cond(W)) is the stability parameter, characterizing the stability of the dimeric complex from the point of view of quantum mechanics. The smaller this parameter, the more stable the biochemical compound and the closer its state to thermodynamic equilibrium.
Next to the wild-type dimer, other dimers containing mutations are shown, for example, or containing small molecules and inhibitors, such as Rigosertib, marked in red in
Figures C and D.
Arrows indicate the direction to thermodynamic equilibrium. Earlier, in experimental studies, it was suggested that the L240F mutation protects microtubules from the effects of rigosertib.
According to our calculations, this assumption has some basis, since tubulins containing this mutation are characterized by a slight decrease in stability when combined with a molecule of Rigosertib compared to wild-type compounds.
Thus, using calculation methods, we can compare the stability of dimeric formations that differ from each other in mutations, as well as in the attached inhibitors and small molecules



Mutations in TBA occur in the lissencephaly disease, and the calculated values are given for dimers containing one mutation in the TBA protein. We interpret the results for the “yellow” mutations as follows:
the more the calculated data for mutant dimers deviate from the calculated data obtained for wild-type dimers, the more noticeable are the differences in the formation and behavior of the assembly of mutant tubulins as a whole.
For example, if we consider the entropic contribution to the formation of a mutant dimer, then the presence of a negative value of the entropy change value may indicate the complexity of the formation and transitions in the formation of such a dimer.

TBA mutations occurring in the specified disease are shown in yellow. The effect of each mutation on dimer assembly, taking into account the addition of a GTP molecule, can be traced in two graphs of calculated values.
Toxic “blue” TBB protein mutations sharply increase the stability of dimer formations, which has a negative effect on the subsequent ability to attach subsequent tubulins.
Negative areas of the entropy change measure also indicate an increase in the orderliness of the mutant dimer system.
How toxic the yellow type of mutations are can be judged from a comparative analysis between two types of mutations with known properties (marked in blue) and mutations that occur in diseases

Dimers characterized by the greatest value of lg(cond(W)) are marked as “unstable”
The stability parameter lg(cond(W)) tends to a minimum under conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium.
lg[Kd]
T(delta)H
The stability parameter lg(cond(W)) tends to a minimum under conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium.
lg[Kd]
T(delta)H
Investigation stability of tubulin dimers upon the addition of various inhibitors: Rigosertib and oN01500
The stability parameter lg(cond(W)) tends to a minimum under conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium.
Also presented are studies of mutant tubulin forms containing a non-toxic mutation and the effect of this mutation on binding to inhibitors.
lg[Kd]
T(delta)H
Blue background shows toxic mutations in TBB during overexpression, yellow background shows mutations in TBA that occur in the disease.
Figures (a),(c), (e), (g)-(i) containe stability information for dimers and tetramers.
Figures (b),(d),(f) contain information about entropy change for dimers and tetramers.

The stability parameter lg(cond(W)) tends to a minimum under conditions of thermodynamic equilibrium.
lg[Kd]
T(delta)H
The first digit represents the stability value, the second blue digit represents the logarithm of the dissociation constant, the third digit represents the change in potential energy as the difference between the energy of the mutant tree and the energy of the wild-type protein. The last digit represents the difference in the rate of change of entropy.
Tubulin proteins can also bind to small molecules and inhibitors, influencing dimer formation and affecting overall stability. The arrows indicate transitions between different states, progressing from less stable to more stable structures.
Understanding these molecular interactions is crucial for biochemistry and pharmaceutical research. Tubulin stability plays a key role in drug development, particularly in cancer therapies that target microtubules.

72 hours post-infection, the cells were mixed 1:1 with uninfected cells and treated with DMSO, increasing concentrations of rigosertib, a pan-PLK inhibitor as a control. Growth curves of the mCherry+ cells that express TUBB L240F and that of mCherry- cells (uninfected controls) is shown in Fig 3A. The results of this study show that both mCherry+ cells that express TUBBL240F or empty vector and mCherry- cells that represent parental cells are inhibited by rigosertib as well as BI2536 in a concentration-dependent manner with very similar kinetics.

[A Contaminant Impurity, Not Rigosertib, Is a Tubulin Binding Agent]




