Braf -Inhibitors
Search for BRAF inhibitors to target mutations in various oncogenic diseases.
Creation of a database of existing small molecules, analysis of their ability to bind to mutant forms of the BRAF protein

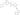

Ponatinib
PHI1



Kinase activity inhibition profiles of BRAFV600E and BRAFWT upon Ponatinib titration using SelectScreen assay.
PHI2 is an analogue of PHI1 with distinct binding specificity for BRAFV600E monomers and dimers compared to PHI1.
(a) The molecular structure of PHI2. (b) BRAF kinase inhibition profiles (SelectScreen, Invitrogen) of PHI2.
(a) The molecular structure of PHI2. (b) BRAF kinase inhibition profiles (SelectScreen, Invitrogen) of PHI2.
Ponatinib induces BRAF dimers with alfaC-CENTER conformation. Crystal structures of BRAF with inhibitors typically are determined in dimeric conformation and each protomer’s бChelix can adopt different conformations between the IN (active) and OUT (inactive) position.
The BRAF–Ponatinib structure corroborates the dimeric conformation of the kinase induced by alfaC-IN inhibitors, with both protomers occupied by Ponatinib [Inhibitors of BRAF dimers using an allosteric site]
PHI1 is selective for oncogenic BRAF dimers.
results demonstrate that PHI1 more effectively targets p61BRAFV600E dimers than BRAFV600E
monomers. [Inhibitors of BRAF dimers using an allosteric site]
results demonstrate that PHI1 more effectively targets p61BRAFV600E dimers than BRAFV600E
monomers. [Inhibitors of BRAF dimers using an allosteric site]
PHI2
Inhibition of kinase activity of BRAFV600E, BRAFWT, and other tyrosine kinases targets, identified by KinomeEDGE®, using SelectScreen (Invitrogen) in the presence of 100 μM ATP. Half-maximal inhibition values (IC50 ± SD) of two technical replicates from n = 2 independent experiments are tabulated. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. [Inhibitors of BRAF dimers using an allosteric site]
CETSA showed that Ponatinib stabilizes BRAFV600E monomers in cells (ΔTm = +6.3 °C) more effectively compared to PHI1 (ΔTm=+3.4 °C)
In contrast, PHI1 and Ponatinib display similar stabilization effect with p61BRAFV600E dimers
(ΔTm=+3.2 °C)
In contrast, PHI1 and Ponatinib display similar stabilization effect with p61BRAFV600E dimers
(ΔTm=+3.2 °C)
A
exhibits discrete cellular selectivity for BRAF dimers, with enhanced inhibition of the second protomer when the first protomer is occupied, comprising a novel class of dimer selective inhibitors.
In melanoma cells expressing BRAFV600E monomers (A375 cells) and constitutively expressed p61BRAFV600E dimers (SKMEL239- C4 cells). The inhibitory activity of PHI1 in A375 cells (IC50 = 2760 nM) is significantly reduced compared to Ponatinib (IC50 = 291 nM), whereas in SKMEL239-C4 (IC50 = 424 nM) it is assessed at similar levels compared to Ponatinib (IC50 = 452 nM). Similar selectivity profiles for Ponatinib (IC50 = 569 nM) and PHI1 (IC50 = 2045 nM) were also observed in SKMEL239 parental cells expressing BRAFV600E monomers.

Consistently, in HEK293 cells ectopically expressing p61BRAFV600E dimers versus p61BRAFV600E harboring the monomer-driver R509H mutation, PHI1 showed preferential inhibition for p61BRAFV600E compared to p61BRAFV600E/R509H BRAF species.
Taken together, these results demonstrate that PHI1 more Effectively targets p61BRAFV600E dimers than BRAFV600ENmonomers.
PHI2 for p61BRAFV600E dimers (SKMEL239-C4 cells) is reduced, while it is increased for BRAFV600E monomers (A375 cells)
B
Mechanisms of RAF inhibitors action. Scheme of four distinct mechanisms of RAF inhibitors action and representative RAF inhibitors for each mechanism. This work revealed that PHI1 displays a distinct structural, inhibitory, and therapeutic mode of action compared to previously characterized αCIN and αC-OUT RAF inhibitors. Moreover, Ponatinib, an FDA-approved inhibitor, is an effective inhibitor of BRAF monomers and RAF dimers with a distinct structural binding mode

C

Schematic depiction of the intramolecular Rluc-PCA–based BRAF kinase conformation reporter (KinCon reporter). Upstream RAS activation (EGF), RAS mutations, RAF mutations, or mutation-specific cancer drugs modulate opened, intermediate, or closed full-length RAF kinase conformations, resulting in an increase or decrease of Rluc-PCA–emitted cellular bioluminescence [BRAF inhibitors promote intermediate BRAF(V600E) conformations and binary interactions with activated RAS]
Impact of indicated BRAFi and MEKi on shown BRAF KinCon reporters (±SEM; n = 9 independent experiments; 3-hour treatments, HEK293 cells).[BRAF inhibitors promote intermediate BRAF(V600E) conformations and binary interactions with activated RAS]

BRAF conformations (alterations of Rluc-PCA bioluminescence) were measured using transiently transfected HEK293 cells. Immunoblotting shows BRAF, F[1]-BRAF-F[2], and F[1]-BRAF(V600E)-F[2] expression levels and P-ERK1/2 levels (representative experiment; ±SD). RLU, relative light units.
D

1. 7WF5//c-Src in complex with ponatinib
2. 4V04//FGFR1 in complex with ponatinib.
3. 4V01//FGFR1 in complex with ponatinib
4. 4UXQ//FGFR4 in complex with Ponatinib
5. 4QRC//Crystal Structure of the Tyrosine Kinase Domain
of FGF Receptor 4 in Complex with Ponatinib
6. 3ZOS//Structure of the DDR1 kinase domain in complex with ponatinib
7.6EG9//IRAK4 in complex with Ponatinib
8. 6P3D//The co-crystal structure of BRAF(V600E) with ponatinib
9. 6TU9//The ROR1 Pseudokinase Domain Bound To Ponatinib
10. 4U0I//Crystal structure of KIT in complex with ponatinib
11. 4C8B//Structure of the kinase domain of human RIPK2
in complex with ponatinib
2. 4V04//FGFR1 in complex with ponatinib.
3. 4V01//FGFR1 in complex with ponatinib
4. 4UXQ//FGFR4 in complex with Ponatinib
5. 4QRC//Crystal Structure of the Tyrosine Kinase Domain
of FGF Receptor 4 in Complex with Ponatinib
6. 3ZOS//Structure of the DDR1 kinase domain in complex with ponatinib
7.6EG9//IRAK4 in complex with Ponatinib
8. 6P3D//The co-crystal structure of BRAF(V600E) with ponatinib
9. 6TU9//The ROR1 Pseudokinase Domain Bound To Ponatinib
10. 4U0I//Crystal structure of KIT in complex with ponatinib
11. 4C8B//Structure of the kinase domain of human RIPK2
in complex with ponatinib
Ponatinib
Src_chick //Src_chick//ponatinib//ponatinib
number condition 3.465104
max eigenvalue ___4.1130392e-19
min eigenvalue____ 1.409478e-22
error computational SVD 2.42770145e-19
number condition 3.465104
max eigenvalue ___4.1130392e-19
min eigenvalue____ 1.409478e-22
error computational SVD 2.42770145e-19
[Structural study of ponatinib in inhibiting SRC kinase]
Statistics Pearson=266.32273
Setting the significance level for the Pearson test=0.050000
Quantile of the distribution Pearson=16.91898
The distribution is chosen incorrectly,since chi^2>chi^2(1-p,n-3)
Statistics Pearson=266.32273
Setting the significance level for the Pearson test=0.001000
Quantile of the distribution Pearson=27.87716
The distribution is chosen incorrectly,since chi^2>chi^2(1-p,n-3)
Setting the significance level for the Pearson test=0.050000
Quantile of the distribution Pearson=16.91898
The distribution is chosen incorrectly,since chi^2>chi^2(1-p,n-3)
Statistics Pearson=266.32273
Setting the significance level for the Pearson test=0.001000
Quantile of the distribution Pearson=27.87716
The distribution is chosen incorrectly,since chi^2>chi^2(1-p,n-3)
7WF5

7wf5
4v04
4v01
4v05
4v04
4v01
4v05
Mutations
number
condition
condition
max value
min value
error computational SVD
2.427e-19
3.589e-19
3.4777e-19
3.0592e-19
3.589e-19
3.4777e-19
3.0592e-19
4.11303e-19
3.2030e-19
3.11726e-19
3.8902e-19
3.2030e-19
3.11726e-19
3.8902e-19
3.4651
4.0046
4.0832
4.8160
4.0046
4.0832
4.8160
1.4097e-19
3.1690e-23
2.573e-23
5.9417e-24
3.1690e-23
2.573e-23
5.9417e-24
C488A;C584S
C488A;C584S
C488A;C584S
PDB

3.99852_____ 3.7517e-19____ 3.7645e-23._ 2.7202e-19
6EG9
F
1.
2.
3.
7.
You can view the full list of values from your laptop or turn on the "Show as on a computer" function.

1. 6P7G//The co-crystal structure of BRAF(V600E) with PHI1
PHI1
Vemurafenib

1.5HES//Human leucine zipper- and sterile alpha motif-containing kinase (ZAK, MLT, HCCS-4, MRK, AZK, MLTK) in complex with vemurafenib
2.5JT2//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically
Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-BISAMIDE
3. 5JRQ//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically
Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-6-VEM
4. 4RZV//Crystal structure of the BRAF (R509H) kinase domain monomer bound to Vemurafenib
5. 5JSM//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-3-VEM
2.5JT2//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically
Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-BISAMIDE
3. 5JRQ//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically
Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-6-VEM
4. 4RZV//Crystal structure of the BRAF (R509H) kinase domain monomer bound to Vemurafenib
5. 5JSM//BRAFV600E Kinase Domain In Complex with Chemically Linked Vemurafenib Inhibitor VEM-3-VEM
G

Dabrafenib
1.4XV9//B-Raf Kinase domain in complex with PLX5568
2. 4XV3//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX7922
4. 4XV2//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with Dabrafenib
3. 4XV1//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX7904
0. 3OG7//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX4032
5.5CSW//B-RAF in complex with Dabrafenib
9. 4V05//FGFR1 in complex with AZD4547.
6.5HIE//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with dabrafenib
7.5HI2//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with sorafenib
8.5C9C//CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BRAF(V600E) IN COMPLEX WITH LY3009120 COMPND
2. 4XV3//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX7922
4. 4XV2//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with Dabrafenib
3. 4XV1//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX7904
0. 3OG7//B-Raf Kinase V600E oncogenic mutant in complex with PLX4032
5.5CSW//B-RAF in complex with Dabrafenib
9. 4V05//FGFR1 in complex with AZD4547.
6.5HIE//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with dabrafenib
7.5HI2//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with sorafenib
8.5C9C//CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BRAF(V600E) IN COMPLEX WITH LY3009120 COMPND

AZ628
GDC0879
GDC0879
1.4RZW//Crystal structure of BRAF (R509H) kinase domain bound to AZ628
2.5HID//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with AZ628
1.7SHV//Crystal structure of BRAF kinase domain bound to GDC0879
2. 4MNF//Crystal structure of BRAF-V600E bound to GDC0879
2.5HID//BRAF Kinase domain b3aC loop deletion mutant in complex with AZ628
1.7SHV//Crystal structure of BRAF kinase domain bound to GDC0879
2. 4MNF//Crystal structure of BRAF-V600E bound to GDC0879
I
You can view the full list of values from your laptop or turn on the "Show as on a computer" function.
Additional background information
6UUO
Crystal structure of BRAF kinase domain bound to the PROTAC P4B
Crystal structure of BRAF kinase domain bound to the PROTAC P4B
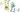
____number condition______________ max________min eigenvalue____error computational SVD
____3.41460399_________________ 3.6546e-19____ 1.4068e-22_______________ 5.36744e-19
____3.41460399_________________ 3.6546e-19____ 1.4068e-22_______________ 5.36744e-19
Binding analysis of small molecule compounds to BRAF
a-d, SPR binding analysis
a-d, SPR binding analysis
wtBRaf
mutBRaf(V600E)
P4B
BI883870
Kd=2,7 (0,3)nM
Kd=3,0 (1,4)nM
Kd=4,7 (0,8)nM
Kd=5,6 (0,7)nM

P4B
K
max RMSD ___________First-Order Optimality Measure
3.8089e-13__________________7.895e-07
3.8089e-13__________________7.895e-07

PDB CHECKING

| | If you are interested in this type of calculations, leave a request and our specialists will contact you shortly on all issues. Meet the group, explore the school, and get a free consultation By sending this request you give your consent to the processing of your data. Website owners have the right to process personal data of clients only after their consent. |

